AIM : How is solubility determined?
Molecular Compounds
-
Follow the "like dissolves like" rule, meaning that polar compounds
will dissolve polar compounds and nonpolar compounds will dissolve
nonpolar compounds
- The solute and solvent need to have similar bonds to mix
Ionic Compounds have a set of rules that can be found in TABLE F of the reference tables:

-This side of the table has ions that are SOLUBLE on the left - This side of the table has ions that are INSOLUBLE on the left
and exceptions to the solubility rules on the right and exceptions to the insolubility rules on the right
ex. halide cmpds are soluble except when it is a silver, lead ex.
carbonate compounds are insoluble except when combined with a Group
1
or mercury halide (FeCl2
is soluble but AgCl is insoluble)
ion or NH4+ ion (CuCO3 is
insoluble but (NH4)2CO3 is soluble)
SOLUBILITY CURVE
- The solubility curve traces the solubility of a substance over a range of temperatures
- The solubility curve helps identify a known solution as saturated or unsaturated
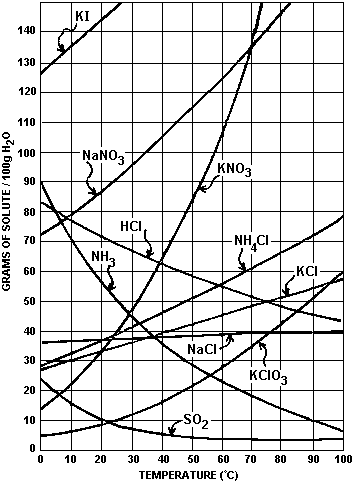
Questions
1) Which salt is least soluble at 20oC?
-ANS = KClO3
-
To find the least soluble substance at a given temperature we follow
the temperature line up and the first substance curve we hit is the
least soluble.
For most soluble it is the same proceedure except the last substance curve hit is the most soluble.
2) At 40oC how much KNO3 can be dissolved in 100g of H2O?
-ANS = about 42gKNO3

