Background Information: An Explantion of the Science and Science Education Ideas in the Lesson and Video
Cardiovascular
disease (CVD) is the leading cause of death for adults ages 65 and older in the
United States. It is the second leading
cause of death for children ages 0-14.
Because of the prevalence of heart disease in the United States, it is imperative
to educate the young population about the risk factors that can lead to one of
the many types of cardiovascular disease.
Our video
shows a variety of common activities that people perform on a daily basis. The video compares healthy and unhealthy
lifestyle choices in hopes of exposing the numerous ways a person can be at
risk of developing cardiovascular disease.
Cardiovascular
Disease is caused by numerous risk factors.
Risk factors include (but are not limited to):
- Alcohol use
- Stress
- Tobacco use
- Sedentary
lifestyle
- Poor
sleeping habits
- Poor nutrition
(i.e. high fat and calorie diet)
- Reclusive behavior (lack
of social interactions)
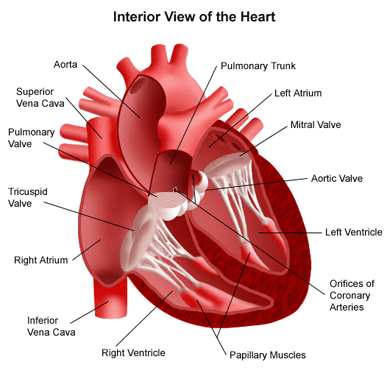
Cardiovascular Disease (CVD)
Cardiovascular
disease (CVD) refers to the class of diseases caused by weakening
and/or malfunction of the heart and blood vessels. There are several types of cardiovascular
diseases, some congenital and others caused by lifestyle choices. The lesson and accompanying class activity
focuses only on the CVDs caused by unhealthy lifestyle choices. A brief description of some of these CVDs follows...
Hypertension
– also known as high blood pressure. This is a condition where the blood
pressure of an individual is chronically elevated, higher than 140/90 (a
systolic pressure greater than 140 and a diastolic pressure greater than 90).
Stroke – This
is a condition characterized as loss of brain function due to a disturbance in
the blood vessel supplying blood to the brain.
It can be caused a blood clot (aka embolism) or hemorrhage (internal
bleeding in the brain).
Aneurysm –
Localized blood filled dilation of a blood vessel, usually an artery, causing weakening
or rupture of the blood vessel. Aneurysms
most commonly occur in the arteries at the base of the brain (called the circle
of Willis) and in the aorta.
Atherosclerosis
–A chronic inflammatory response in the arterial walls, due to build-up of LDL
(low-density lipoprotein cholesterol).
This accumulation of cholesterol hardens the blood vessels and could
eventually break, forming a free-floating blood clot. Atherosclerosis typically begins in early
adolescence.
Pericardial
Disease (aka Percarditis) – This condition is characterized as inflammation of
the membrane surrounding the heart (pericardium).
Angina –
Chest pains caused by a lack of oxygen supply to the muscles of the heart, most
commonly caused by obstruction or spasm of the coronary arteries (the blood
vessels that supply blood to the heart). Coronary artery disease is the main cause of
angina.
Congestive
Heart Failure – A condition that results from a structural or functional cardiac
disorder that impairs the ability of the heart to fill with or pump a
sufficient amount of blood to the body.
Valvular
Heart Disease – A class of diseases that affects one or more valves of the
heart; may be congenital or acquired.
Coronary
Artery Disease – This is the disease of the arteries that provide oxygen and
nutrients to the muscles of the heart. This
CVD is the number one cause of death for men and women ages 65 and older.
Cardiomyopathy
–deterioration of the function of heart muscle (myocardium), for any reason.
Myocardial
Infarction – also known as heart attack. This condition occurs when the blood
supply to part of the heart is interrupted, which can cause damage and/or death
of heart tissue.