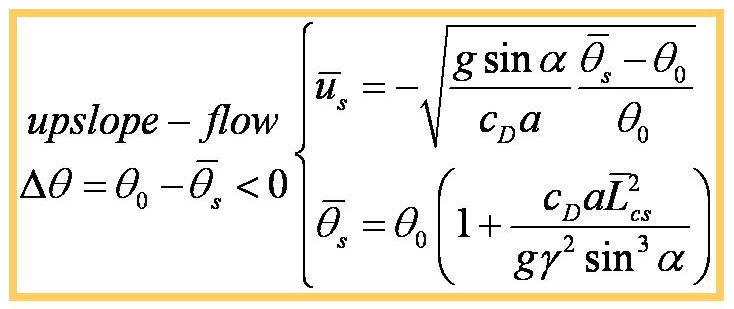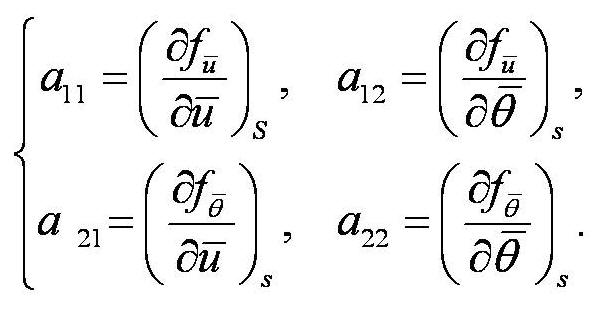|
Stabilities of Terrain-Induced Canopy Flows
The terrain-induced flows often result in a
complicated situation in measurements of trace gas exchanges between
vegetation and atmosphere. The stability analysis on the
terrain-induced canopy flows is the key to understanding the
introduction of pollutants into the atmosphere and the transfer of
water from soil and vegetation to the atmosphere. An analytical
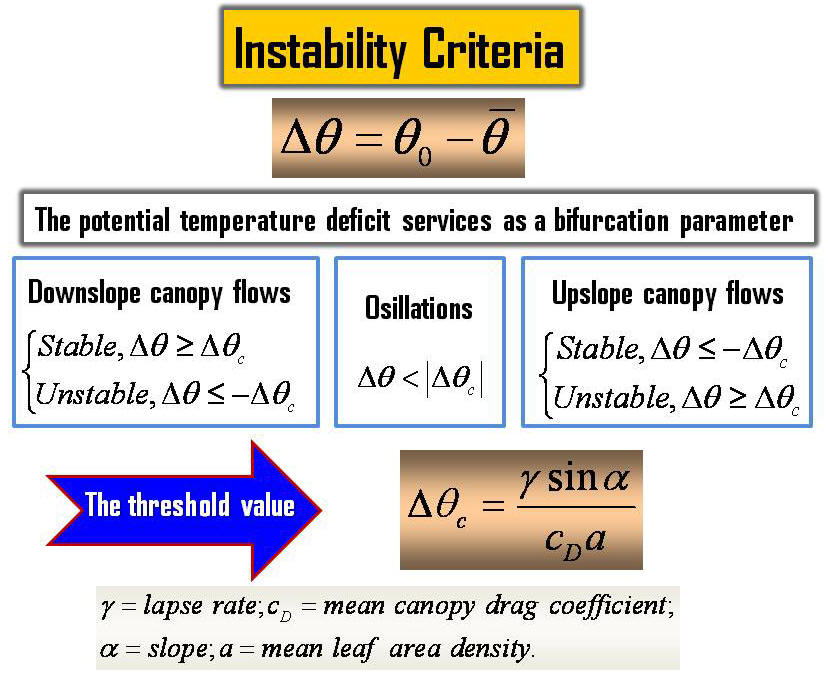
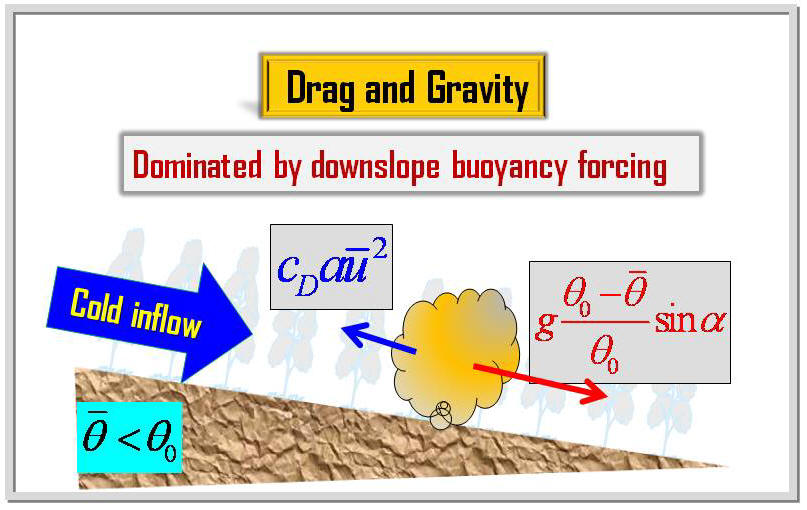
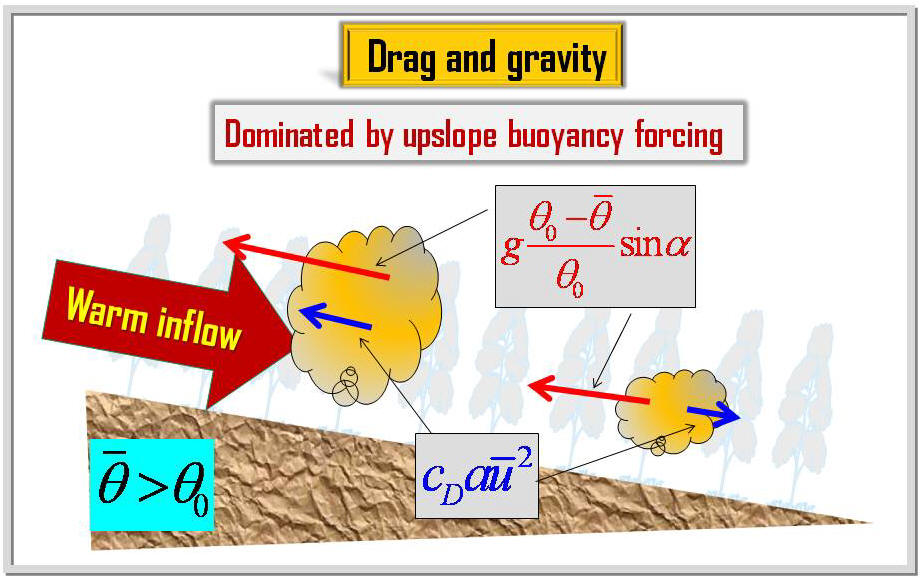
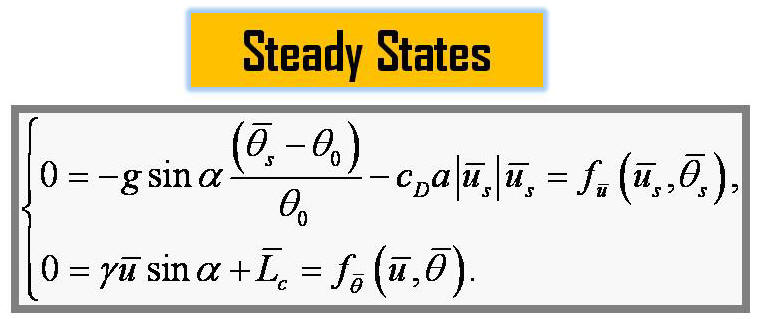
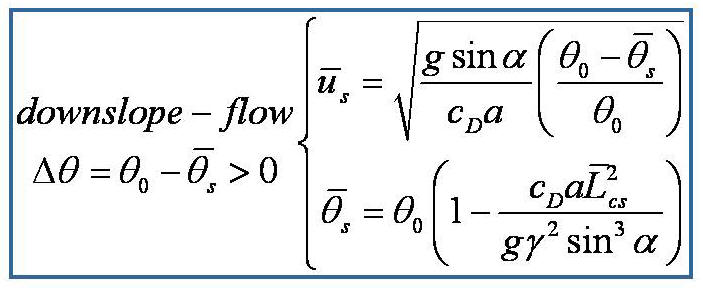
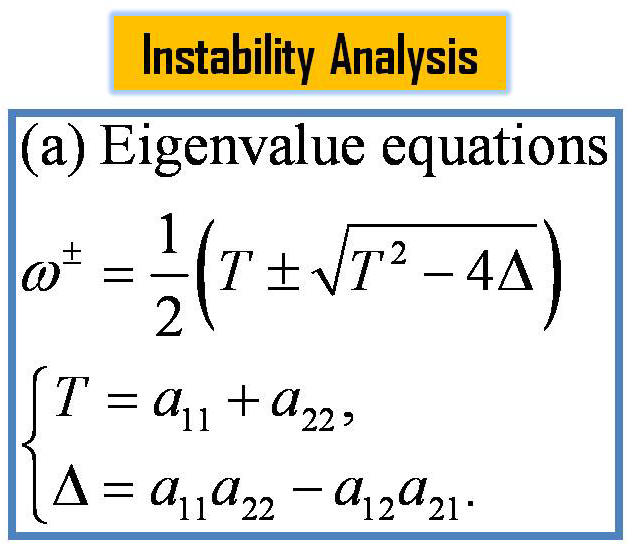
criterion of instability of the terrain-induced canopy flows is
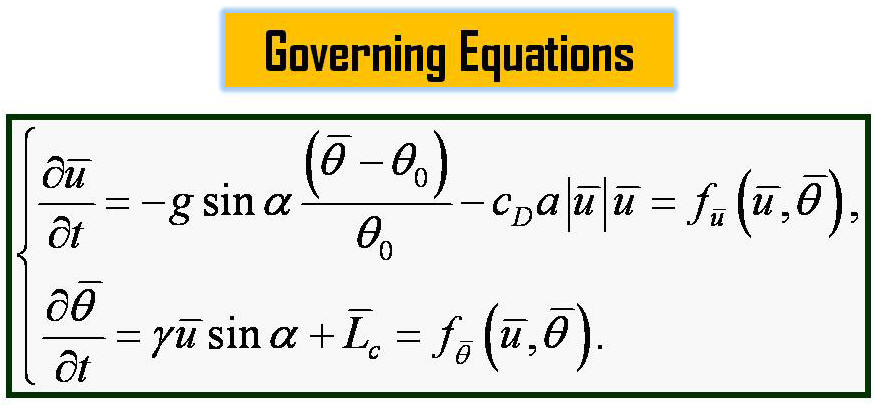
derived from the simplified thermal-hydro-mechanical equations by
nonlinear dynamics approach. The analytical stability criterion is
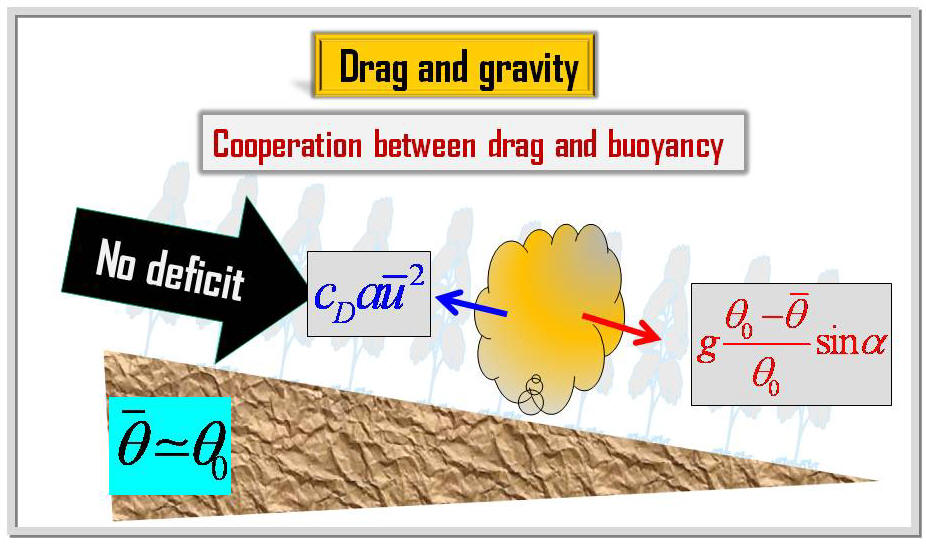
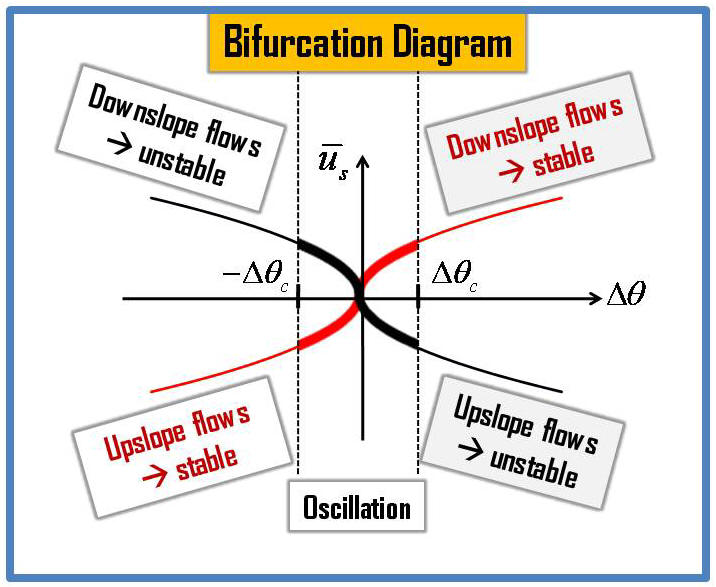
determined from the terrain slope, environmental lapse rate, drag
coefficient, and leaf area density of vegetation. The stability of
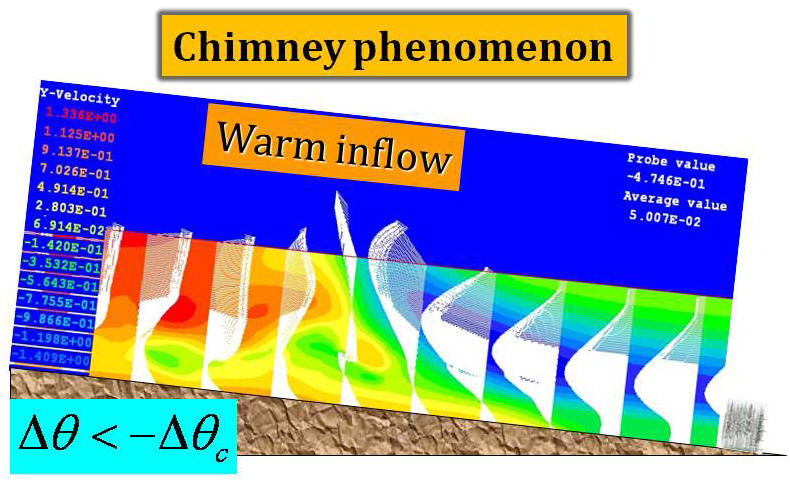
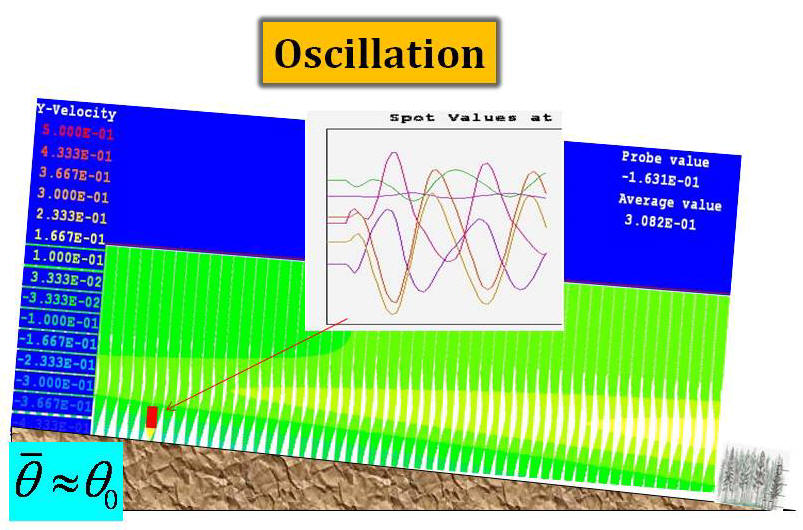
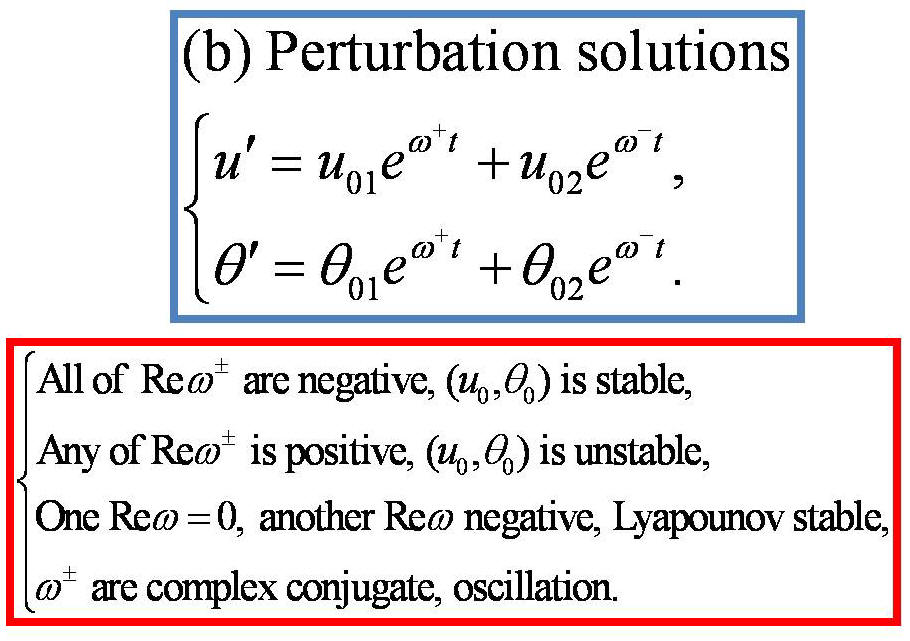
the terrain-induced canopy flows and an oscillation solution are
predicted based on the instability-criterion. These predictions are
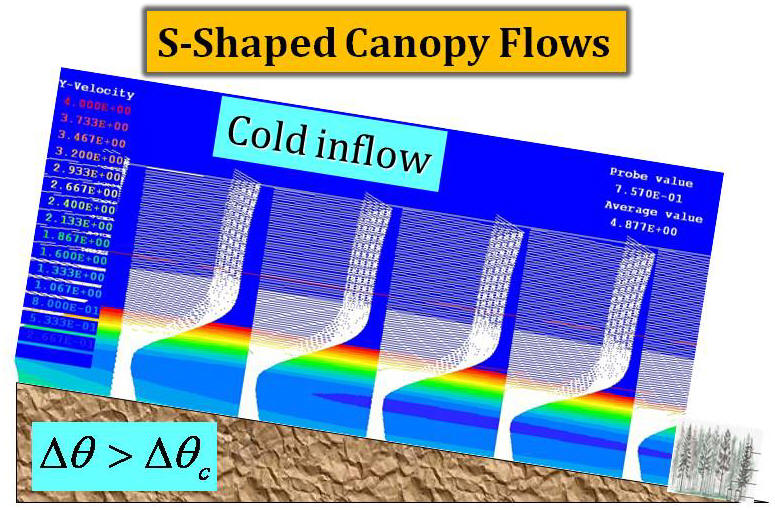
tested against the numerical simulations by the computational fluid
dynamics (CFD) approach based on thermal-hydro-mechanical equations.
Yi, C., Instability analysis of terrain-induced canopy flows, Journal of the Atmospheric Sciences, 66, 2134-2142, doi:10.1175/2009JAS3005.1, 2009.[Print Version] Yi, C., Momentum transfer within canopies, Journal of Applied Meteorology and Climatology, 47, 262-275, doi:10.1175/2007JAMC1667.1, 2008. [Print Version]
Yi, C.,
R. K. Monson, Z. Zhai,
D. E. Anderson, B. Lamb, G. Allwine, A. A. Turnipseed, and S. P.
Burns, Modeling and measuring the nocturnal drainage flow in a
high-elevation, subalpine forest with complex terrain, Journal
of Geographical Research, 110, D22303,
doi:10.1029/2005JD006282, 2005. [Print
Version]
|
 |
|
 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|