|
|
|
| Home | Personnel | Research | Publications | Current Offering | |
|
CFD modeling |
|||||
|
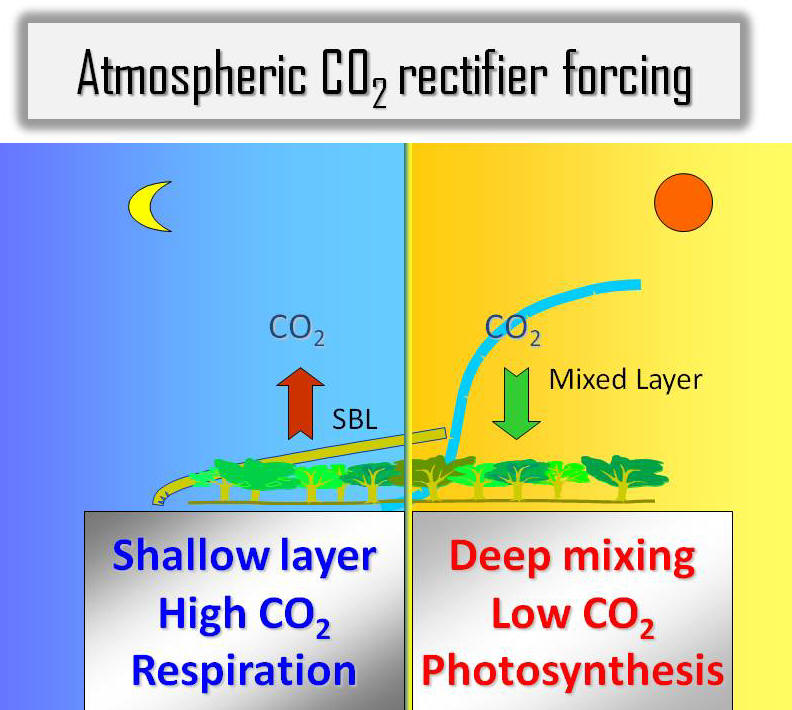
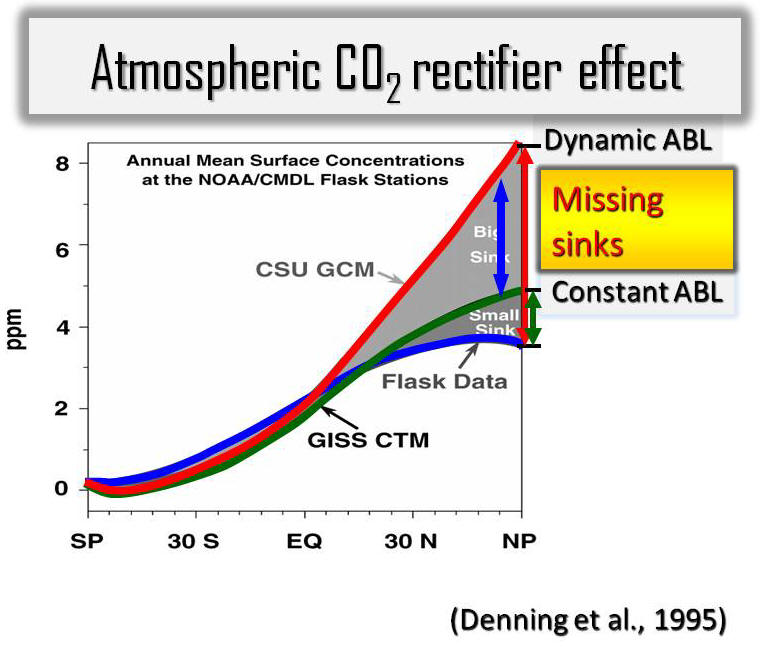
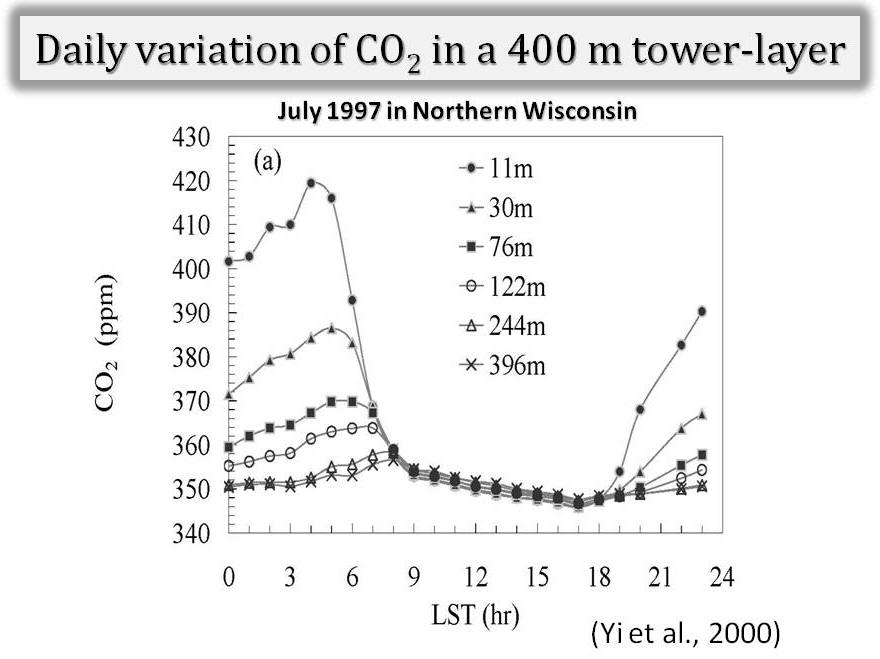
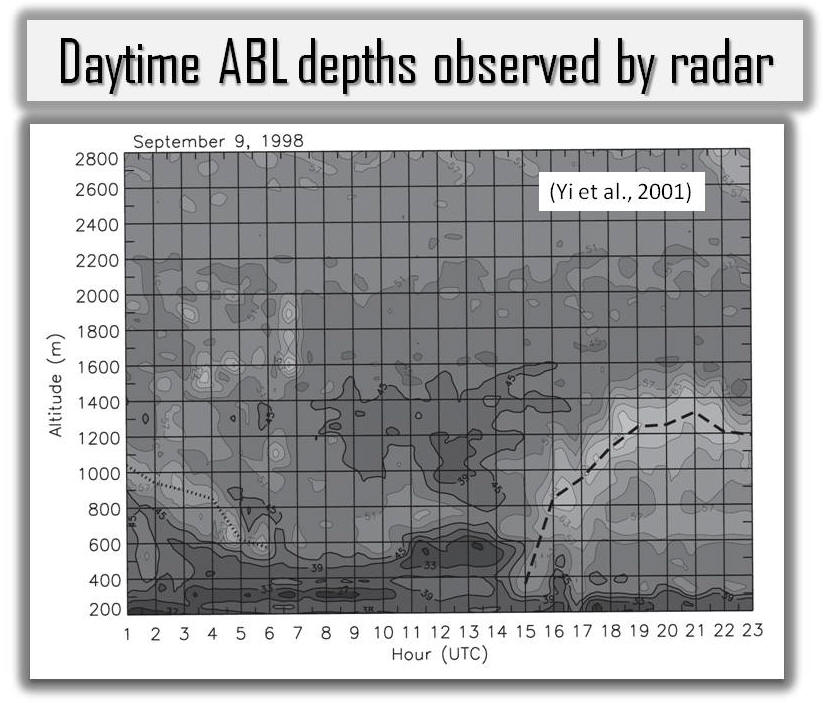
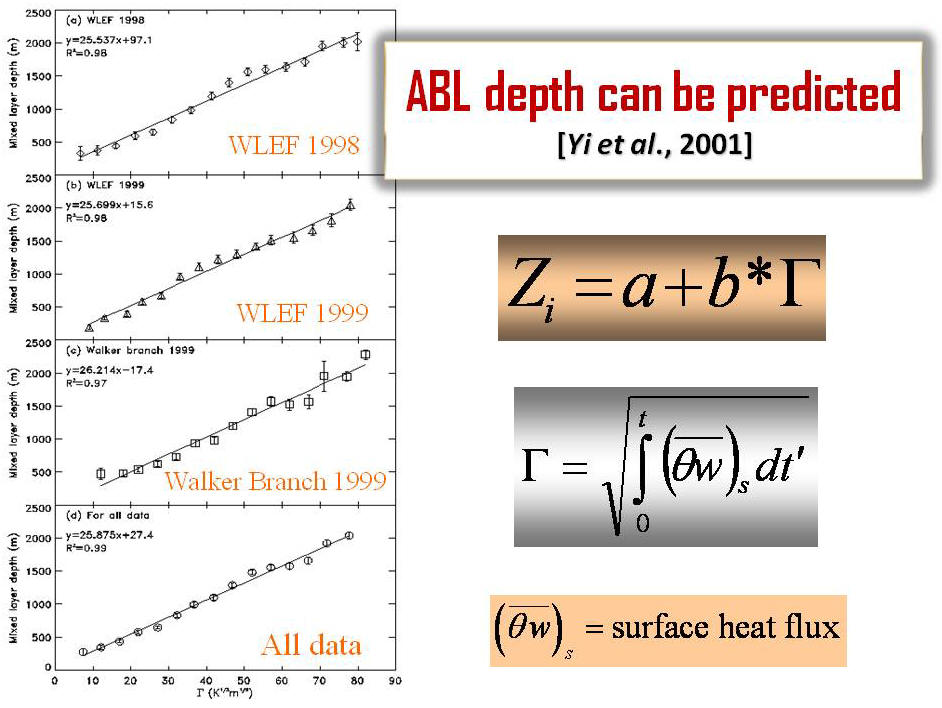
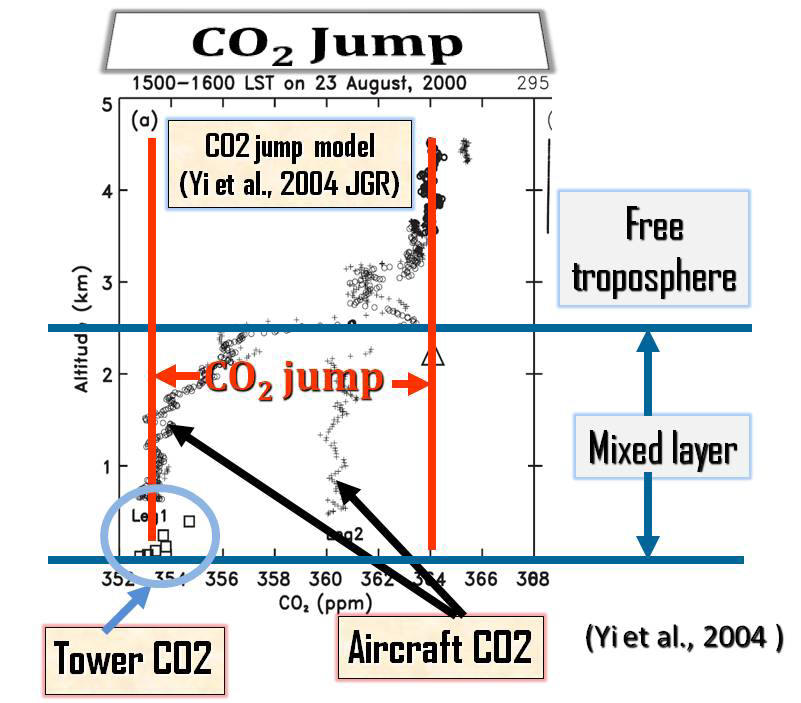
Atmospheric Rectifier Effect Yi, C., K. J. Davis, B. W. Berger, P. S. Bakwin, Long-term observations of the dynamics of the continental planetary boundary layer, Journal of the Atmospheric Science, 58, 1288-1299, 2001. [Print Version] Salcido, A., Celada-Murillo, A.-T., Carreón-Sierra, S., Castro, T., Peralta, O., Salcido-González, R.-S., Hernández-Flores, N., Tamayo-Flores, G.-A., Martínez-Flores, M.-A. (2020). Estimations of the Mexicali Valley (Mexico) Mixing Height. Atmosphere,, 11, 505. PDF Yi, C., K. J. Davis, P. S. Bakwin, A.S. Denning, N. Zhang, A. Desai, J. C. Lin, and C. Gerbig, The observed covariance between ecosystem carbon exchange and atmospheric boundary layer dynamics at a site in northern Wisconsin, Journal of Geophysical Research, 109, D08302, doi:10.1029/2003JD004164, 2004. [Print Version] Yi, C., K. J. Davis, P. S. Bakwin, B. W. Berger, and L. Marr, The influence of advection on measurements of the net ecosystem-atmosphere exchange of CO2 from a very tall tower, Journal of Geophysical Research , 105, 9991-9999, 2000. [Print Version] Denning, A.S., N. Zhang, C. Yi, M. Branson, K. Davis, J. Kleist, and P. Bakwin, Evaluation of modeled atmospheric boundary layer depth at the WLEF Tower, Agricultural and Forest Meteorology, 148, 206-215, 2008. [Print Version] Bakwin, P.S., K.J. Davis, C. Yi, S.C. Wofsy, J.W. Munger, L. Haszpra and Z. Barcza, Regional carbon dioxide fluxes from mixing ratio data, Tellus 56B, 301-311, 2004. [Print Version] |